Mastering English Tenses: A Complete Information with Utilization Chart
Associated Articles: Mastering English Tenses: A Complete Information with Utilization Chart
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Mastering English Tenses: A Complete Information with Utilization Chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering English Tenses: A Complete Information with Utilization Chart

English tenses is usually a daunting facet of the language, particularly for learners. Nevertheless, understanding their nuances and acceptable utilization is essential for clear and efficient communication. This text supplies a complete information to English tenses, full with an in depth utilization chart, examples, and explanations that can assist you grasp this important grammatical factor.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Time and Facet
Earlier than diving into particular tenses, it is important to know the core ideas: time and facet.
- Time: This refers to when an motion takes place – previous, current, or future.
- Facet: This describes how an motion unfolds in time. It may be:
- Easy: A normal assertion concerning the motion.
- Steady (Progressive): An motion in progress at a selected time.
- Good: An motion accomplished earlier than a selected time limit.
- Good Steady (Progressive): An motion in progress that was accomplished earlier than a selected time limit.
The Twelve Major Tenses
English grammar sometimes identifies twelve fundamental tenses, every combining time and facet. These are categorized into three fundamental time frames: previous, current, and future. Inside every time-frame, we’ve the straightforward, steady, excellent, and ideal steady features.
1. Current Tense:
- Current Easy: Used for ordinary actions, normal truths, and unchanging conditions.
- Instance: I eat breakfast each morning. The solar rises within the east.
- Current Steady: Used for actions occurring now, momentary actions, and future preparations.
- Instance: I am consuming breakfast now. She is finding out for her examination this week. They are leaving tomorrow.
- Current Good: Used for actions accomplished at an unspecified time previously, actions with a outcome within the current, and actions that began previously and proceed to the current.
- Instance: I have eaten breakfast. She has lived in London for 5 years.
- Current Good Steady: Used for actions that began previously and proceed to the current, emphasizing the period of the motion.
- Instance: I have been finding out English for 3 years. They have been working on that mission all week.
2. Previous Tense:
- Previous Easy: Used for accomplished actions previously.
- Instance: I ate breakfast this morning. She went to the park yesterday.
- Previous Steady: Used for actions in progress at a selected time previously.
- Instance: I was consuming breakfast when the cellphone rang. They have been enjoying soccer at 3 pm.
- Previous Good: Used for actions accomplished earlier than one other motion previously.
- Instance: I had eaten breakfast earlier than I left for work. She had completed her homework earlier than she went out.
- Previous Good Steady: Used for actions in progress earlier than one other motion previously, emphasizing the period.
- Instance: I had been finding out for hours earlier than I lastly understood the idea. They had been ready for ages earlier than the bus arrived.
3. Future Tense:
- Future Easy (will): Used for predictions, guarantees, spontaneous selections, and normal future occasions.
- Instance: I will eat breakfast tomorrow. It will rain later. I will assist you with that.
- Future Steady (will probably be -ing): Used for actions in progress at a selected time sooner or later.
- Instance: I will probably be consuming dinner at 7 pm. They will probably be enjoying soccer tomorrow afternoon.
- Future Good (could have -ed): Used for actions accomplished earlier than a selected time sooner or later.
- Instance: I could have completed my work by 5 pm. She could have graduated by subsequent June.
- Future Good Steady (could have been -ing): Used for actions in progress earlier than a selected time sooner or later, emphasizing the period.
- Instance: I could have been finding out English for 5 years by subsequent yr. They could have been residing in Paris for ten years by then.
Additional Issues:
- Modal Verbs: Phrases like can, might, might, would possibly, ought to, would, should specific risk, capacity, permission, obligation, and many others., and are sometimes used with different tenses to change their that means. For instance, "I can go" (current capacity), "I might go" (previous capacity or risk), "I ought to go" (obligation or recommendation).
- Passive Voice: The passive voice focuses on the motion quite than the actor. It is fashioned utilizing a type of "to be" + previous participle. For instance, "The cake was eaten" (previous easy passive). The passive voice can be utilized with all tenses.
- Irregular Verbs: Many verbs have irregular previous tense and previous participle kinds (e.g., go, went, gone). Studying these irregular verbs is important for correct tense utilization.
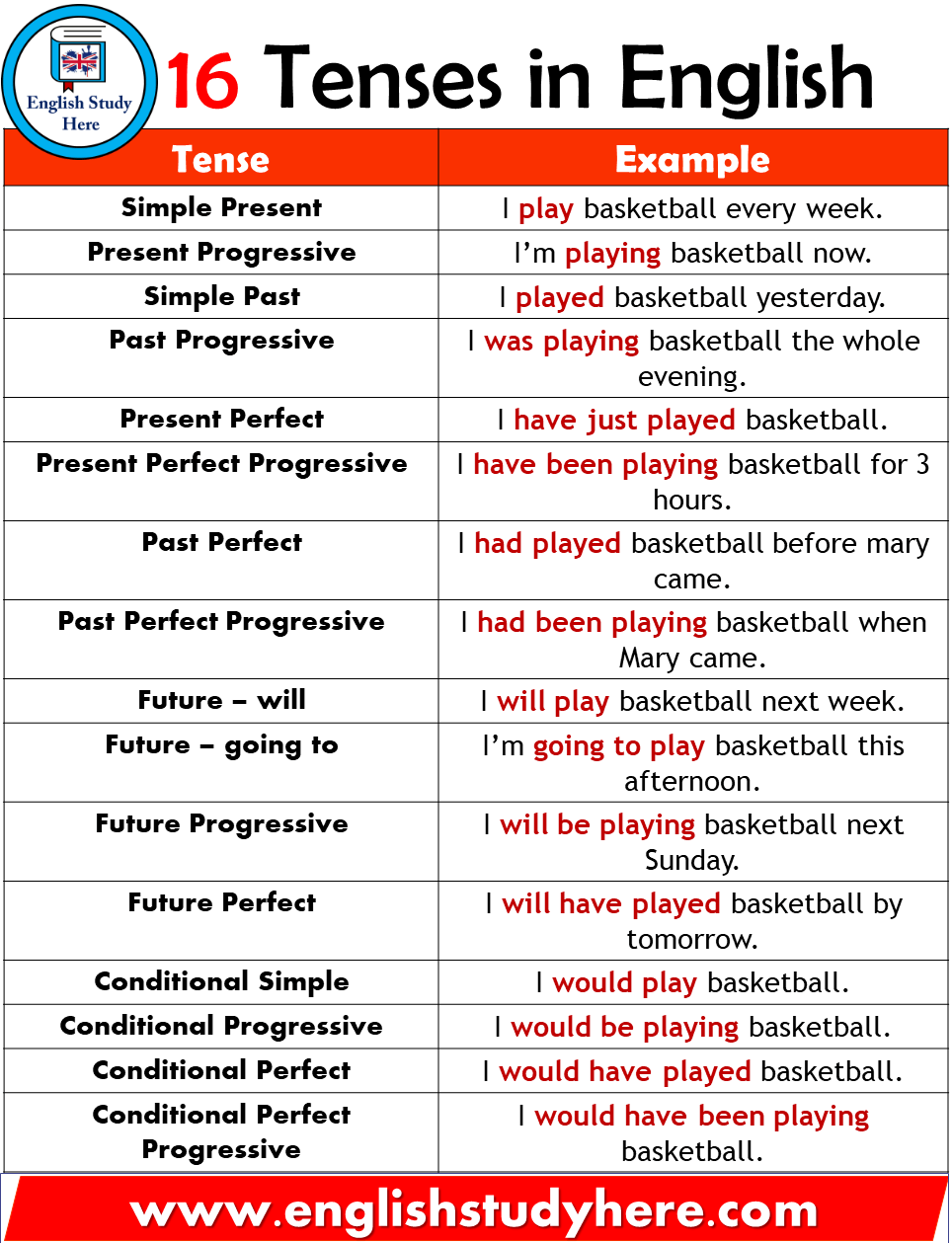
Tense Utilization Chart:
| Tense | Time | Facet | Kind | Instance | Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Easy | Current | Easy | Base kind (add -s/-es for third particular person) | I eat. He eats. | Habits, routines, normal truths, information |
| Current Steady | Current | Steady | am/is/are + -ing | I’m consuming. He’s consuming. | Actions occurring now, momentary actions, future preparations |
| Current Good | Current | Good | have/has + previous participle | I’ve eaten. She has eaten. | Actions accomplished at unspecified time, lead to current, ongoing since previous |
| Current Good Steady | Current | Good Steady | have/has + been + -ing | I’ve been consuming. She has been consuming. | Actions ongoing since previous, emphasizing period |
| Previous Easy | Previous | Easy | Previous tense kind | I ate. He ate. | Accomplished actions previously |
| Previous Steady | Previous | Steady | was/have been + -ing | I used to be consuming. They have been consuming. | Actions in progress at a selected time previously |
| Previous Good | Previous | Good | had + previous participle | I had eaten. She had eaten. | Actions accomplished earlier than one other previous motion |
| Previous Good Steady | Previous | Good Steady | had + been + -ing | I had been consuming. That they had been consuming. | Actions in progress earlier than one other previous motion, emphasizing period |
| Future Easy | Future | Easy | will + base kind | I’ll eat. He’ll eat. | Predictions, guarantees, spontaneous selections, normal future occasions |
| Future Steady | Future | Steady | will probably be + -ing | I will probably be consuming. He will probably be consuming. | Actions in progress at a selected time sooner or later |
| Future Good | Future | Good | could have + previous participle | I’ll have eaten. He could have eaten. | Actions accomplished earlier than a selected time sooner or later |
| Future Good Steady | Future | Good Steady | could have been + -ing | I’ll have been consuming. He could have been consuming. | Actions in progress earlier than a selected time sooner or later, emphasizing period |
This complete information and chart present a stable basis for understanding and utilizing English tenses successfully. Constant follow and a focus to context are key to mastering these grammatical buildings and speaking clearly and precisely in English. Bear in mind to seek the advice of grammar sources and follow often to solidify your understanding.



.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Mastering English Tenses: A Complete Information with Utilization Chart. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!