Charts and Graphs: A Deep Dive into Visible Information Illustration
Associated Articles: Charts and Graphs: A Deep Dive into Visible Information Illustration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Charts and Graphs: A Deep Dive into Visible Information Illustration. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Charts and Graphs: A Deep Dive into Visible Information Illustration

Charts and graphs are ubiquitous in our data-driven world. From monetary stories and scientific publications to social media dashboards and information articles, they function highly effective instruments for speaking complicated info concisely and successfully. Whereas usually used interchangeably, charts and graphs are distinct but associated visible representations of knowledge, every with its personal strengths and functions. Understanding their variations and selecting the suitable visualization is essential for clear and impactful communication.
Defining the Phrases: Charts vs. Graphs
The excellence between "chart" and "graph" is not rigidly outlined throughout all disciplines. Some sources use them synonymously, whereas others preserve a delicate however vital distinction. Typically talking:
-
Chart: A chart is a broader time period encompassing varied visible representations of knowledge designed as an instance relationships, developments, and patterns. Charts usually make the most of a mix of visible components like bars, traces, pie slices, or icons to characterize information factors. They sometimes emphasize the general image and key takeaways quite than exact numerical particulars.
-
Graph: A graph, in a extra technical sense, refers particularly to a visible illustration of knowledge utilizing factors, traces, and curves to indicate the connection between two or extra variables. Graphs are sometimes used to depict steady information and spotlight developments or correlations. They emphasize the exact numerical relationship between information factors.
This distinction highlights the core distinction: charts prioritize a holistic view, whereas graphs deal with the exact relationships between variables. Nevertheless, this distinction isn’t at all times strictly adhered to, and the phrases are sometimes used interchangeably, notably in casual contexts.
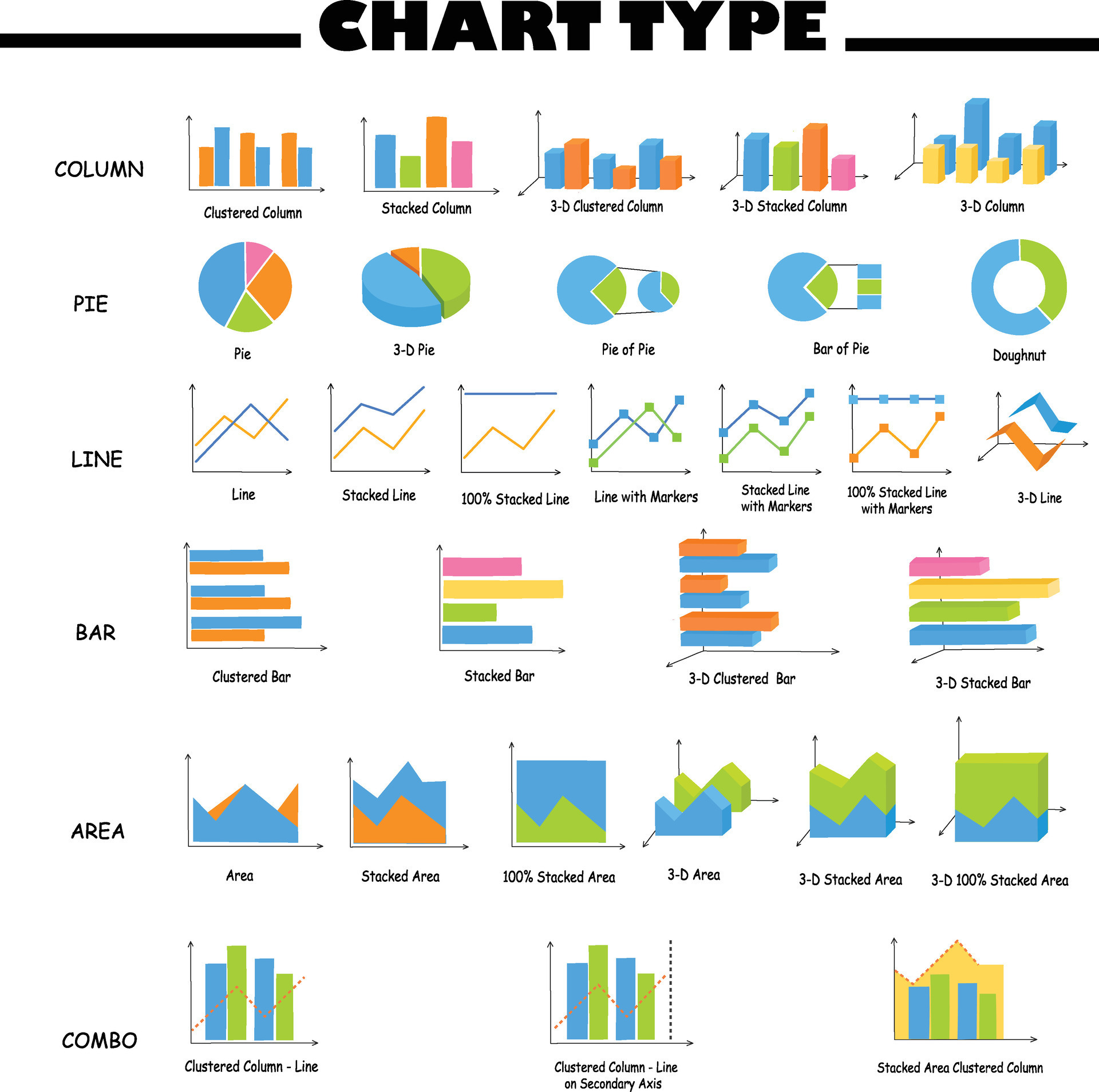
Sorts of Charts and Their Functions:
The world of charts is numerous, with quite a few varieties designed for particular information and communication targets. Some widespread examples embrace:
-
Bar Charts: Supreme for evaluating discrete classes or teams. They use rectangular bars of various lengths to characterize information values, making it straightforward to visually evaluate magnitudes. Variations embrace clustered bar charts (evaluating a number of teams inside classes) and stacked bar charts (exhibiting the composition of an entire).
-
Pie Charts: Efficient for exhibiting the proportion of components to a complete. Every slice represents a class’s proportion of the overall, offering a fast visible understanding of relative contributions. Nevertheless, they turn out to be much less efficient with quite a few classes.
-
Line Charts: Finest suited to visualizing developments and adjustments over time or steady information. They use related traces to depict information factors, revealing patterns and fluctuations. A number of traces can be utilized to check totally different developments concurrently.
-
Space Charts: Much like line charts, however the space below the road is crammed, emphasizing the magnitude of change over time. They’re notably helpful for highlighting cumulative values or totals.
-
Scatter Plots: Used as an instance the connection between two variables. Every information level is represented by a dot, revealing correlations, clusters, and outliers. They’re worthwhile for exploring potential relationships and figuring out patterns.
-
Pictograms: Use icons or photographs to characterize information values, making them visually interesting and simply comprehensible, notably for non-technical audiences. Nevertheless, they are often much less exact than different chart varieties.
-
Flowcharts: Illustrate processes or workflows utilizing a collection of interconnected shapes and arrows. They’re important for visualizing sequential steps and resolution factors.
-
Gantt Charts: Used for challenge administration to visually characterize duties, durations, and dependencies over time. They facilitate scheduling and monitoring progress.
Sorts of Graphs and Their Functions:
Whereas the time period "graph" is commonly used broadly, particular varieties throughout the broader class of visible information illustration embrace:
-
Line Graphs: These are sometimes thought-about a subset of each charts and graphs, as mentioned earlier. They emphasize the continual relationship between variables, notably over time.
-
Scatter Plots (as Graphs): As talked about above, scatter plots are additionally generally thought-about a sort of graph, specializing in the connection between two variables utilizing factors in a coordinate system.
-
Community Graphs: Visualize relationships between entities, similar to folks, organizations, or web sites. Nodes characterize entities, and edges characterize connections between them. They’re helpful for visualizing complicated networks and figuring out key gamers or clusters.
-
Tree Diagrams: Illustrate hierarchical relationships, similar to organizational buildings or resolution timber. They use branching buildings to indicate the relationships between dad or mum and baby nodes.
Selecting the Proper Visualization:
The important thing to efficient information communication lies in deciding on the suitable chart or graph for the particular information and meant viewers. Take into account the next components:
- Kind of Information: Discrete vs. steady, categorical vs. numerical.
- Variety of Information Factors: Too many information factors would possibly overwhelm a easy chart.
- Message to Convey: Traits, comparisons, proportions, correlations, and many others.
- Viewers Understanding: Technical vs. non-technical viewers.
For instance, a bar chart is right for evaluating gross sales figures throughout totally different areas, whereas a line chart is healthier for exhibiting web site visitors over time. A pie chart successfully illustrates the market share of various firms, whereas a scatter plot helps reveal the correlation between promoting spend and gross sales income.
Past the Fundamentals: Enhancing Visualizations
Efficient charts and graphs transcend merely displaying information; they inform a narrative. A number of strategies improve their influence:
- Clear Labeling: Axes, titles, legends, and information labels ought to be clear and concise.
- Acceptable Scaling: Keep away from deceptive scales that distort the information.
- Constant Formatting: Preserve constant colours, fonts, and kinds.
- Highlighting Key Findings: Use annotations, callouts, or shade coding to emphasise vital developments or patterns.
- Contextual Data: Present ample background info to assist the viewers perceive the information.
Conclusion:
Charts and graphs are important instruments for speaking information successfully. Whereas the excellence between the 2 phrases could be blurry, understanding their nuances and selecting the suitable visualization is essential for clear and impactful communication. By rigorously contemplating the kind of information, the meant message, and the viewers, we will create compelling visuals that reveal insights, assist arguments, and drive knowledgeable decision-making. The power to pick out and interpret these visualizations is an important ability in right now’s data-rich atmosphere. Mastering the artwork of visible information illustration empowers us to unlock the facility of knowledge and talk its tales successfully.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Charts and Graphs: A Deep Dive into Visible Information Illustration. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!