Earlier than You Slice the Pie: A Complete Information to Charting Your Knowledge with Pie Charts
Associated Articles: Earlier than You Slice the Pie: A Complete Information to Charting Your Knowledge with Pie Charts
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Earlier than You Slice the Pie: A Complete Information to Charting Your Knowledge with Pie Charts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Earlier than You Slice the Pie: A Complete Information to Charting Your Knowledge with Pie Charts

Pie charts, with their visually interesting round segments, are a staple of information visualization. Their simplicity makes them look like an easy alternative for displaying proportions, however a poorly constructed pie chart could be extra complicated than useful. Earlier than you even start to contemplate the colours and labels, a number of essential questions have to be addressed to make sure your pie chart successfully communicates your information and avoids frequent pitfalls. This complete information explores these important questions, offering a framework for creating correct, informative, and visually compelling pie charts.
1. Is a Pie Chart the Proper Selection?
That is maybe probably the most essential query. Whereas pie charts excel at displaying the relative proportions of components to a complete, they’ve limitations. Earlier than committing to a pie chart, think about these alternate options and their strengths:
-
Bar Charts: Bar charts are sometimes superior for evaluating the magnitude of various classes, particularly when the variations between proportions are refined. They’re simpler to learn exactly and permit for higher comparability of values.
-
Stacked Bar Charts: These charts are much like bar charts however stack segments representing totally different classes on prime of one another inside a single bar. They’re helpful for displaying each the person contribution of every class and the whole sum.
-
Treemaps: These charts characterize hierarchical information utilizing nested rectangles, the place the world of every rectangle is proportional to the worth it represents. They’re significantly efficient for visualizing complicated hierarchical information units.
-
Donut Charts: These are variations of pie charts which have a gap within the middle, usually used to show extra data or a abstract statistic. They are often extra visually interesting and simpler to label than pie charts, significantly with many segments.
A pie chart is greatest suited when:
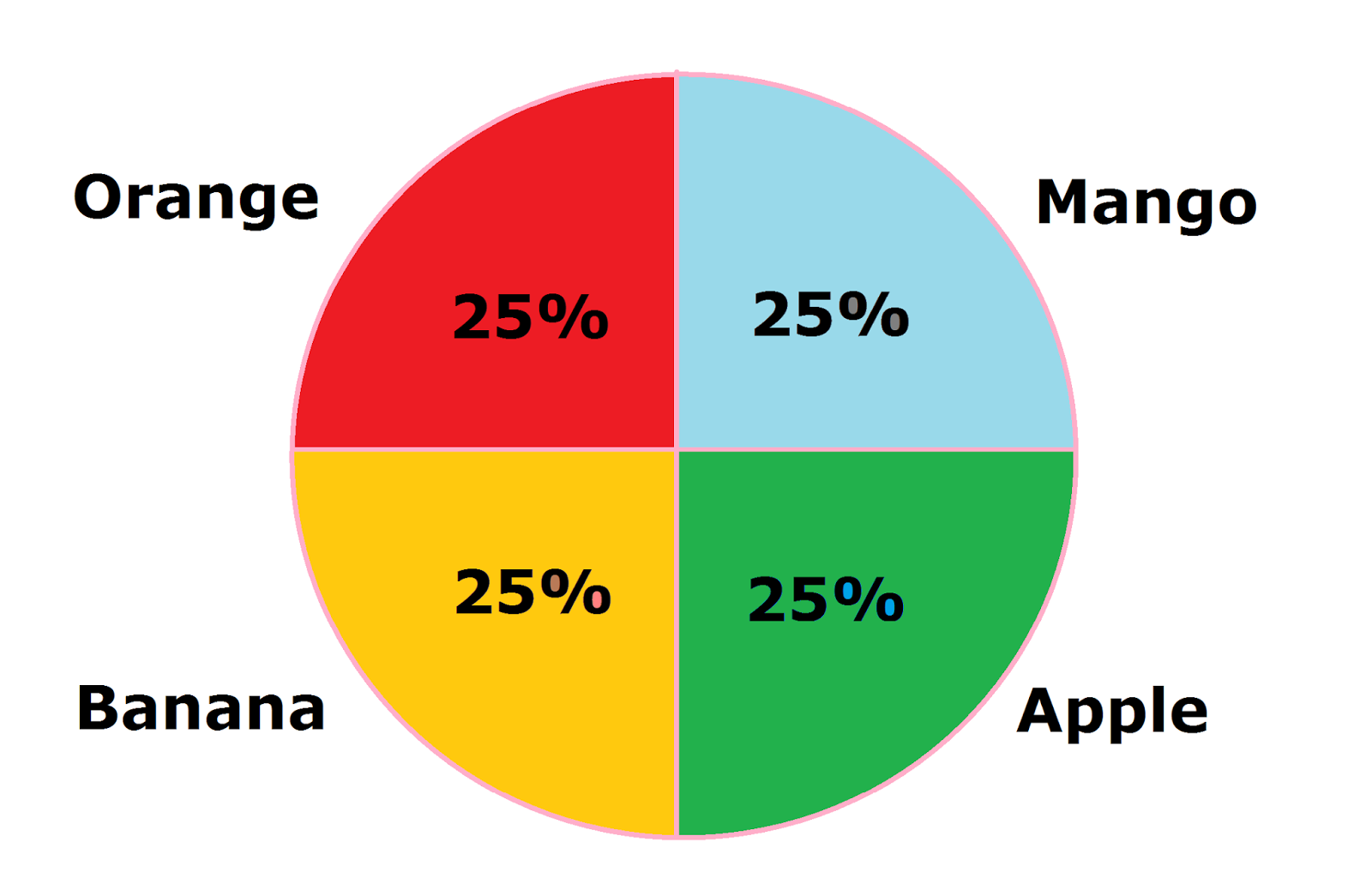
- The variety of classes is comparatively small (ideally, fewer than 7): Too many segments make the chart cluttered and tough to interpret.
- The variations between the proportions are visually distinct: If the proportions are very comparable, a pie chart may not successfully spotlight the variations.
- The main target is on the relative proportions of the entire: If absolutely the values are additionally necessary, a distinct chart sort is likely to be extra applicable.
In case your information does not meet these standards, rethink your alternative of visualization. A poorly chosen chart can mislead the viewers and undermine the effectiveness of your information presentation.
2. What’s Your Knowledge Telling You? Defining the "Entire" and its Parts.
Earlier than even touching a spreadsheet, you want a transparent understanding of your information. What’s the "entire" you are making an attempt to characterize? What are the person elements that make up this entire? This appears apparent, however a scarcity of readability at this stage can result in errors in information preparation and interpretation.
For instance, for those who’re analyzing gross sales figures for various product classes, the "entire" is the whole gross sales, and the elements are the gross sales for every product class. Guarantee your information is precisely categorized and that each one elements are included within the "entire." Lacking information or incorrect categorization will distort the proportions in your pie chart.
3. Knowledge Cleansing and Preparation: Guaranteeing Accuracy and Consistency.
As soon as you have outlined your "entire" and its elements, the following step is meticulous information cleansing and preparation. This includes:
- Checking for errors: Establish and proper any inconsistencies or errors in your information. This would possibly contain reviewing information entry, checking for outliers, and addressing lacking values.
- Knowledge transformation: You would possibly want to remodel your information to make sure it is appropriate for a pie chart. For instance, you would possibly must calculate percentages or proportions based mostly on the whole.
- Knowledge aggregation: When you have too many classes, think about aggregating them into broader teams to cut back the variety of segments in your pie chart. This must be completed rigorously and transparently, guaranteeing the aggregation logic is evident and justifiable.
Correct information is the muse of a dependable pie chart. Neglecting this stage can result in deceptive conclusions.
4. Selecting the Proper Software program and Instruments:
A number of software program packages and instruments can create pie charts. The selection is determined by your technical expertise and the complexity of your information. Choices embrace:
- Spreadsheet software program (Excel, Google Sheets): These are readily accessible and user-friendly choices for creating fundamental pie charts.
- Knowledge visualization software program (Tableau, Energy BI): These supply extra superior options, permitting for interactive charts, customizability, and integration with different information sources.
- Programming languages (Python, R): These present probably the most management and adaptability, permitting for the creation of extremely personalized and complicated charts.
Whatever the instrument you select, guarantee it permits for correct labeling, clear legends, and the flexibility to customise the looks of your chart to enhance readability.
5. Labeling and Legend: Clear Communication is Key.
The labels in your pie chart are essential for understanding the information. Every phase ought to be clearly labeled with its corresponding class and its share of the entire. Keep away from overly lengthy labels; abbreviate if essential, however make sure the abbreviations are simply comprehensible.
A legend can be necessary, particularly you probably have many segments or if the labels aren’t instantly on the segments. The legend ought to clearly hyperlink the colours or patterns used within the chart to the corresponding classes.
6. Visible Aesthetics: Enhancing Readability and Attraction.
Whereas a pie chart’s simplicity is interesting, visible aesthetics play an important position in its effectiveness. Contemplate these factors:
- Colour Palette: Select a coloration palette that’s visually interesting and simple to differentiate. Keep away from utilizing too many colours, particularly you probably have many segments. Think about using colorblind-friendly palettes.
- Phase Ordering: Organize the segments in a logical order, maybe from largest to smallest or by another related criterion.
- Exploded Segments: You’ll be able to "explode" a number of segments to emphasise specific classes, however use this sparingly, as overuse could make the chart cluttered.
- 3D Results: Keep away from 3D results, as they’ll distort the notion of proportions.
The aim is to create a visually interesting chart that’s simple to grasp and interpret with out sacrificing accuracy.
7. Context and Interpretation: Presenting the Story.
A pie chart is not only a visible illustration of information; it is a instrument for speaking a narrative. Earlier than presenting your chart, think about:
- Goal Viewers: Tailor the complexity and stage of element to your viewers’s understanding.
- Contextual Info: Present ample context to assist the viewers perceive the information and its implications.
- Limitations: Acknowledge any limitations of your information or the chart itself. For instance, point out if sure information factors are lacking or if the classes are aggregated.
A well-crafted pie chart, introduced with applicable context and interpretation, generally is a highly effective instrument for speaking insights and driving knowledgeable decision-making. Nevertheless, neglecting these essential pre-charting issues can result in misinterpretations, deceptive conclusions, and a missed alternative to successfully talk your information’s story. Keep in mind, the aim is evident, correct, and impactful communication – not only a fairly image.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Earlier than You Slice the Pie: A Complete Information to Charting Your Knowledge with Pie Charts. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!