Decoding the Smith Chart: A Deep Dive into Impedance Matching and the Energy of Calculators
Associated Articles: Decoding the Smith Chart: A Deep Dive into Impedance Matching and the Energy of Calculators
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Smith Chart: A Deep Dive into Impedance Matching and the Energy of Calculators. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Smith Chart: A Deep Dive into Impedance Matching and the Energy of Calculators

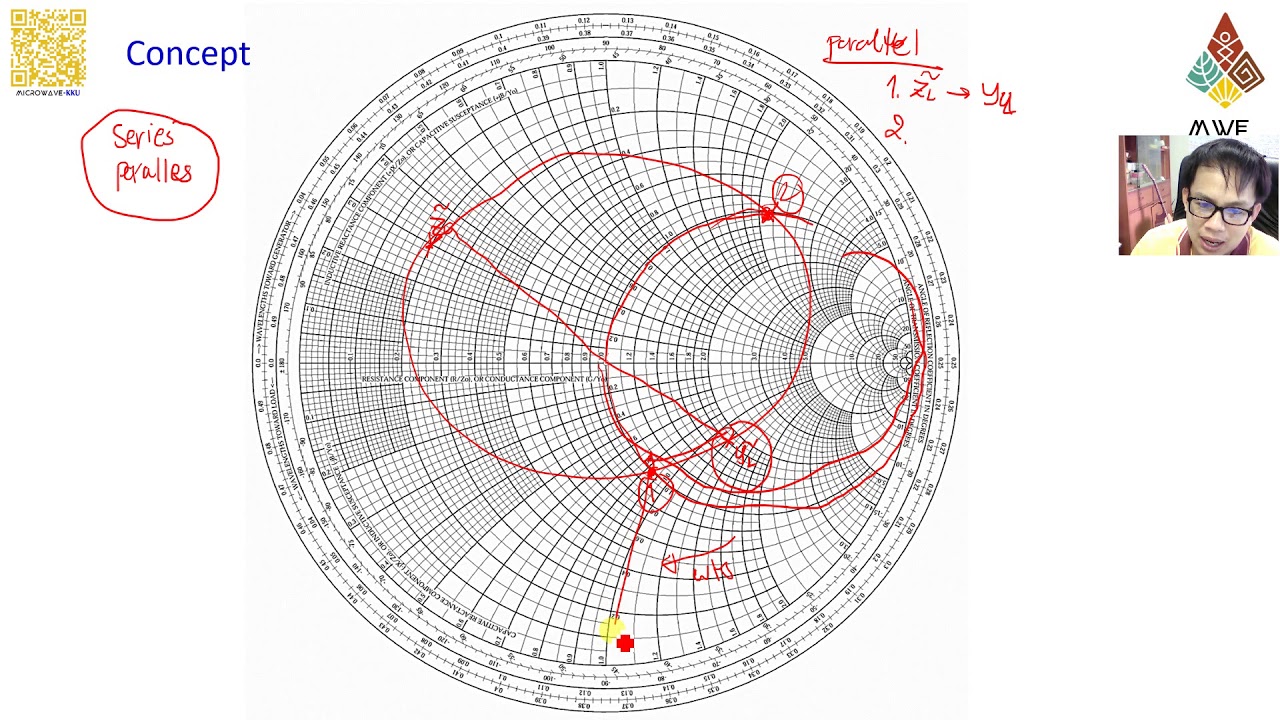
The Smith Chart, a seemingly arcane graphical instrument, is a cornerstone of high-frequency engineering. For many years, it has been the go-to technique for visualizing and fixing impedance matching issues in radio frequency (RF) and microwave circuits. Whereas trendy software program packages provide refined simulations, understanding the Smith Chart stays essential for insightful evaluation and fast problem-solving. This text will discover the basics of the Smith Chart, its functions, and the numerous function of Smith Chart calculators in simplifying its use.
Understanding the Smith Chart: A Graphical Illustration of Impedance
The Smith Chart, conceived by Phillip H. Smith in 1939, is a polar plot that represents advanced impedance (or admittance) normalized to a attribute impedance (normally 50 ohms). As an alternative of plotting impedance instantly on a Cartesian aircraft, it cleverly maps your complete vary of doable normalized impedances onto a single circle. This compact illustration permits for a visible understanding of impedance transformations and matching methods.
The chart’s key options embody:
-
Outer Circle: Represents the fixed resistance circles. The middle represents a normalized resistance of 1 (equal to the attribute impedance). Circles nearer to the middle characterize decrease resistances, whereas these nearer to the periphery characterize increased resistances.
-
Radial Traces: Characterize fixed reactance traces. Traces extending to the precise characterize optimistic reactance (inductive), whereas these extending to the left characterize damaging reactance (capacitive).
-
Unit Circle: The outer circle, also called the unit circle, encloses all doable normalized impedances. Factors exterior this circle characterize impedances with a normalized resistance larger than 1.
Why Use a Smith Chart?
The Smith Chart gives a number of benefits over purely mathematical calculations:
-
Visible Illustration: It provides a transparent, graphical visualization of impedance transformations. The impact of including parts like inductors and capacitors may be seen immediately.
-
Simplified Calculations: Many impedance matching issues may be solved graphically on the Smith Chart with minimal calculations, particularly for easy matching networks.
-
Intuitive Understanding: The chart fosters a greater understanding of the relationships between impedance, reflection coefficient, and transmission line parameters.
-
Matching Community Design: It aids within the design of matching networks to optimize energy switch between supply and cargo.
The Reflection Coefficient: The Bridge Between Impedance and the Smith Chart
The Smith Chart is essentially primarily based on the reflection coefficient (Γ), a posh quantity that represents the ratio of the mirrored wave to the incident wave at a given impedance. The reflection coefficient is said to the normalized impedance (Zn) by:
Γ = (Zn – 1) / (Zn + 1)
This equation is the mathematical basis of the Smith Chart. Every level on the chart corresponds to a singular worth of Γ, and therefore a singular impedance. The magnitude of Γ represents the diploma of mismatch, whereas its angle represents the part of the reflection.
Utilizing a Smith Chart Calculator: Streamlining the Course of
Whereas the Smith Chart is highly effective, handbook calculations and plotting may be time-consuming and vulnerable to errors. That is the place Smith Chart calculators are available in. These calculators, obtainable as each standalone software program and on-line instruments, considerably simplify the method:
-
Automated Calculations: They mechanically calculate the reflection coefficient and impedance from user-defined values.
-
Interactive Plotting: They supply an interactive graphical illustration of the Smith Chart, permitting customers to visualise impedance transformations and matching networks in real-time.
-
Part Addition: Many calculators permit the addition of parts (inductors, capacitors) and instantly present their impact on the impedance and reflection coefficient.
-
Matching Community Synthesis: Superior calculators may even help within the design of matching networks, suggesting acceptable element values to attain optimum impedance matching.
-
Varied Codecs: Fashionable calculators typically assist completely different impedance codecs (e.g., Cartesian, polar) and frequency ranges.
Functions of Smith Chart Calculators:
Smith Chart calculators are invaluable in a variety of RF and microwave functions, together with:
-
Antenna Design: Optimizing antenna impedance matching for environment friendly energy switch.
-
Microwave Circuit Design: Designing matching networks for amplifiers, oscillators, and different microwave parts.
-
Transmission Line Evaluation: Analyzing the impedance traits of transmission traces and figuring out standing wave ratios.
-
Excessive-Frequency Measurement: Decoding impedance measurements from community analyzers and different check gear.
-
Schooling and Coaching: Offering a user-friendly platform for studying and understanding Smith Chart ideas.
Selecting the Proper Smith Chart Calculator:
When choosing a Smith Chart calculator, take into account the next elements:
-
Options: Does it provide the options you want, akin to element addition, matching community synthesis, and completely different impedance codecs?
-
Ease of Use: Is the interface intuitive and user-friendly?
-
Accuracy: Is the calculator dependable and correct in its calculations?
-
Platform Compatibility: Is it appropriate along with your working system and different software program?
-
Value: Are there any related prices, akin to subscription charges?
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Smith Chart Methods
The Smith Chart’s capabilities lengthen past primary impedance matching. Superior methods embody:
-
Admittance Smith Charts: These charts characterize admittance as an alternative of impedance, which is beneficial in sure circuit evaluation eventualities.
-
Stability Circles: These circles determine areas of stability for amplifiers and oscillators.
-
Fixed Acquire Circles: These circles assist in the design of amplifiers with particular achieve traits.
-
Noise Circles: These circles help within the design of low-noise amplifiers.
Conclusion:
The Smith Chart stays a robust instrument for RF and microwave engineers regardless of the provision of refined software program. Its graphical nature gives invaluable insights into impedance matching and circuit conduct. Smith Chart calculators additional improve its utility by automating calculations, simplifying the design course of, and making it accessible to a broader vary of customers. Whether or not you are a seasoned engineer or a pupil studying the basics, mastering the Smith Chart and using a dependable calculator is essential for fulfillment in high-frequency design. The power to rapidly visualize impedance transformations and design matching networks is a ability that continues to be extremely beneficial within the ever-evolving discipline of RF and microwave engineering. As expertise advances, so too will the capabilities of Smith Chart calculators, persevering with to make this basic instrument much more highly effective and accessible.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Decoding the Smith Chart: A Deep Dive into Impedance Matching and the Energy of Calculators. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!