Understanding and Using X-Y Axis Charts: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using X-Y Axis Charts: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Using X-Y Axis Charts: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using X-Y Axis Charts: A Complete Information
The Cartesian coordinate system, named after René Descartes, varieties the muse of numerous charts and graphs used to visualise information throughout varied disciplines. At its coronary heart lies the straightforward but highly effective idea of the x-axis and y-axis, permitting us to symbolize relationships between two variables in a transparent and simply interpretable method. This text delves deep into the world of x-y axis charts, exploring their varied sorts, functions, and the essential issues for efficient information visualization.
The Fundamentals: X-Axis and Y-Axis
The x-axis, also called the horizontal axis, usually represents the impartial variable. That is the variable that’s manipulated or managed in an experiment or research. It’s typically used to symbolize time, classes, or every other variable that does not immediately depend upon the opposite variable being plotted.
The y-axis, or vertical axis, represents the dependent variable. That is the variable that’s measured or noticed and is predicted to vary in response to adjustments within the impartial variable. It typically displays the end result, impact, or response being studied.
The intersection of the x-axis and y-axis is known as the origin, representing the purpose (0,0). Every axis is scaled appropriately to accommodate the vary of values for the respective variables. The scales may be linear (equal intervals between markings) or logarithmic (intervals enhance exponentially), relying on the character of the information.
Kinds of X-Y Axis Charts
A number of chart sorts make the most of the x-y axis framework, every fitted to completely different information sorts and functions:
-
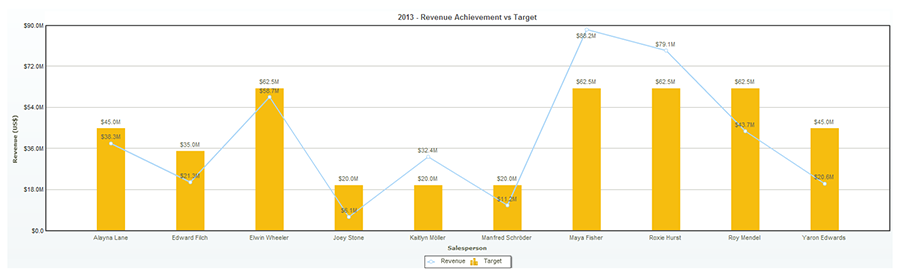
Line Charts: Ultimate for displaying traits and adjustments over time or throughout steady variables. Information factors are related by strains, highlighting the development or relationship between the variables. Line charts are notably helpful for visualizing time collection information, reminiscent of inventory costs, temperature fluctuations, or inhabitants progress. A number of strains may be plotted on the identical chart to match completely different datasets.
-
Scatter Plots: Used to show the connection between two variables with out implying causality. Every information level is represented as a dot on the chart, and the general sample of the factors reveals the correlation (or lack thereof) between the variables. Scatter plots are glorious for figuring out outliers, clusters, and potential traits. They’re regularly utilized in statistical evaluation to discover correlations and match regression fashions.
-
Bar Charts: Signify information utilizing rectangular bars, with the size of every bar similar to the worth of the variable. Bar charts are efficient for evaluating discrete classes or teams. They’re generally used to indicate variations in gross sales figures throughout completely different product strains, inhabitants counts throughout completely different areas, or the frequency of assorted occasions. Horizontal bar charts are typically most popular when class labels are lengthy.
-
Space Charts: Just like line charts, however the space beneath the road is stuffed with coloration. This emphasizes the magnitude of the values and is useful for visualizing cumulative totals or proportions over time. Stacked space charts enable for the comparability of a number of variables contributing to a complete.
-
Bubble Charts: Lengthen the performance of scatter plots by including a 3rd dimension utilizing the dimensions of the bubbles. The scale of every bubble represents the worth of a 3rd variable, making it potential to visualise three variables concurrently on a two-dimensional chart. Bubble charts are efficient for displaying relationships between variables with various magnitudes.
Selecting the Proper Chart Sort
The choice of the suitable x-y axis chart relies upon closely on the character of the information and the message to be conveyed. Take into account the next components:
-
Sort of Variables: Are the variables steady or discrete? Steady variables (e.g., temperature, weight) are finest represented by line charts or scatter plots, whereas discrete variables (e.g., classes, counts) are higher fitted to bar charts.
-
Relationship between Variables: Is there a causal relationship, a correlation, or just a comparability between variables? Line charts spotlight traits and adjustments over time, scatter plots discover correlations, and bar charts examine classes.
-
Variety of Variables: What number of variables have to be visualized? Scatter plots and bubble charts can deal with three variables, whereas different chart sorts are usually restricted to 2.
-
Viewers and Goal: Who’s the meant viewers, and what’s the objective of the visualization? A easy bar chart could be ample for a basic viewers, whereas a extra advanced chart with a number of strains or bubbles could be crucial for a specialised viewers or an in depth evaluation.
Efficient Information Visualization with X-Y Axis Charts
Creating efficient x-y axis charts includes a number of key issues:
-
Clear and Concise Labels: Axes must be clearly labeled with the variable names and models of measurement. Items must be constant all through the chart.
-
Applicable Scale: The size of every axis must be chosen to precisely symbolize the information with out distorting the visible impression. Logarithmic scales may be useful for information with a variety of values.
-
Legend: If a number of datasets are plotted on the identical chart, a transparent and concise legend is crucial for distinguishing between them.
-
**






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Understanding and Using X-Y Axis Charts: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!