Unveiling Information: A Complete Information to Bar Graphs, Histograms, Line Graphs, and Pie Charts
Associated Articles: Unveiling Information: A Complete Information to Bar Graphs, Histograms, Line Graphs, and Pie Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling Information: A Complete Information to Bar Graphs, Histograms, Line Graphs, and Pie Charts. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling Information: A Complete Information to Bar Graphs, Histograms, Line Graphs, and Pie Charts
Information visualization is the cornerstone of efficient communication in quite a few fields, from scientific analysis and enterprise analytics to journalism and on a regular basis life. Understanding and decoding knowledge is essential, however uncooked numbers usually fail to convey that means successfully. That is the place knowledge visualization instruments like bar graphs, histograms, line graphs, and pie charts step in, reworking complicated datasets into simply digestible visible representations. This text delves into the specifics of every chart kind, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and applicable purposes.
1. Bar Graphs: Evaluating Classes with Readability
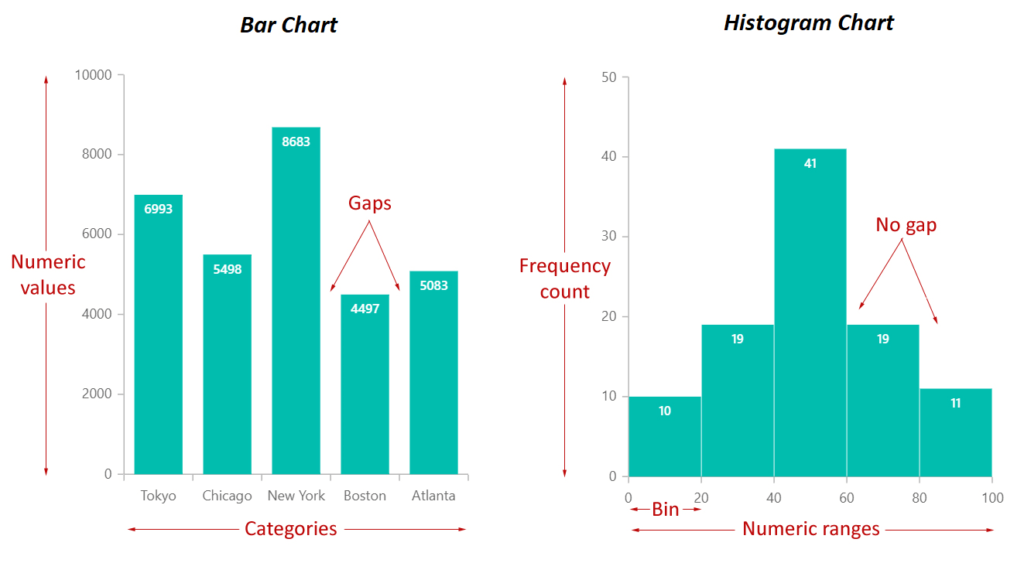
Bar graphs, also referred to as bar charts, are maybe essentially the most widely known and simply understood knowledge visualization software. They are perfect for evaluating discrete classes or teams. Every class is represented by an oblong bar, with the bar’s size proportional to the worth it represents. Bar graphs may be vertical (with bars extending upwards) or horizontal (with bars extending sideways), relying on desire and the character of the information.
Strengths of Bar Graphs:
- Simplicity and Readability: Their simple design makes them simple to grasp, even for people with restricted statistical data.
- Efficient Comparability: They excel at displaying variations between classes, permitting for fast identification of the most important and smallest values.
- Versatile Utility: They can be utilized to symbolize a variety of information, from gross sales figures and inhabitants statistics to survey outcomes and experimental outcomes.
- Straightforward to Create: Quite a few software program packages and on-line instruments make creating bar graphs a easy course of.
Weaknesses of Bar Graphs:
- Restricted to Discrete Information: They aren’t appropriate for representing steady knowledge (knowledge that may tackle any worth inside a spread).
- Tough to Present Developments Over Time: Whereas doable, displaying temporal traits shouldn’t be their major energy. Line graphs are higher fitted to this objective.
- Overcrowding with Many Classes: If there are too many classes, the graph can turn into cluttered and tough to interpret.
Instance: A bar graph might successfully illustrate the gross sales figures for various product traces in an organization over a particular quarter, clearly displaying which product carried out greatest and worst.
2. Histograms: Unveiling the Distribution of Steady Information
Histograms are carefully associated to bar graphs however serve a definite objective. Whereas bar graphs evaluate discrete classes, histograms show the distribution of steady knowledge. As a substitute of particular person classes, histograms use bins (intervals or ranges) to group knowledge factors. The peak of every bar represents the frequency (or depend) of information factors falling inside that specific bin.
Strengths of Histograms:
- Visualizing Information Distribution: They supply a transparent image of how knowledge is unfold throughout a spread of values, revealing patterns like skewness (asymmetry) and modality (variety of peaks).
- Figuring out Outliers: Excessive values (outliers) may be simply noticed, highlighting potential anomalies within the knowledge.
- Understanding Information Form: Histograms enable for the identification of information distributions similar to regular, uniform, skewed, or bimodal distributions.
Weaknesses of Histograms:
- Bin Measurement Issues: The selection of bin measurement considerably impacts the looks of the histogram. An inappropriate bin measurement can obscure vital particulars or create deceptive interpretations.
- Not Ideally suited for Comparisons: In contrast to bar graphs, histograms aren’t designed for direct comparability of various classes.
- Might be Misinterpreted: With out correct understanding of the underlying knowledge and the implications of bin measurement, histograms may be simply misinterpreted.
Instance: A histogram might successfully present the distribution of pupil examination scores, revealing the typical rating, the unfold of scores, and the presence of any outliers (extraordinarily excessive or low scores).
3. Line Graphs: Tracing Developments Over Time
Line graphs are particularly designed for instance traits and adjustments in knowledge over time or throughout a steady variable. They use related factors to symbolize knowledge values, with the x-axis usually representing time or one other steady variable, and the y-axis representing the measured worth.
Strengths of Line Graphs:
- Present Developments and Patterns: They’re wonderful for visualizing traits, displaying will increase, decreases, and intervals of stability.
- Highlighting Adjustments Over Time: They’re significantly helpful for displaying knowledge collected over time, similar to inventory costs, temperature fluctuations, or financial development.
- Straightforward to Interpret Adjustments: The slope of the road clearly signifies the speed of change. A steep slope signifies a fast change, whereas a flat line signifies stability.
Weaknesses of Line Graphs:
- Not Ideally suited for Evaluating Classes: They’re much less efficient for evaluating completely different classes than bar graphs.
- Might be Cluttered with A number of Traces: When displaying a number of knowledge units, the graph can turn into tough to interpret if not correctly organized and labeled.
- Can Misrepresent Information: Improper scaling of the axes can create a deceptive impression of the pattern.
Instance: A line graph would successfully visualize the expansion of an organization’s income over a number of years, showcasing intervals of fast growth and slower development.
4. Pie Charts: Exhibiting Proportions inside a Entire
Pie charts are round diagrams that symbolize proportions or percentages of a complete. The circle is split into slices, with every slice representing a class and its measurement proportional to its share of the entire.
Strengths of Pie Charts:
- Visualizing Proportions: They’re wonderful for displaying the relative measurement of various elements of a complete.
- Straightforward to Perceive: Their visible nature makes them simply comprehensible, even for these unfamiliar with statistical ideas.
- Efficient for Easy Datasets: They’re simplest when representing a small variety of classes.
Weaknesses of Pie Charts:
- Tough to Evaluate Slices Exactly: Exact comparisons between slices may be difficult, particularly when the variations are small.
- Restricted to a Single Dataset: They’re usually used to symbolize a single dataset, making it tough to match a number of datasets concurrently.
- Ineffective with Many Classes: With too many classes, the chart turns into cluttered and tough to interpret.
Instance: A pie chart might successfully symbolize the completely different age teams inside a inhabitants, displaying the proportion of every age group relative to the whole inhabitants.
Conclusion:
Selecting the suitable chart kind relies on the character of the information and the message you wish to convey. Bar graphs excel at evaluating discrete classes, histograms reveal the distribution of steady knowledge, line graphs observe adjustments over time, and pie charts illustrate proportions inside an entire. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of every chart kind is essential for creating efficient and insightful knowledge visualizations that talk info clearly and precisely. Whereas software program can automate the creation of those charts, a robust understanding of their objective and limitations is crucial for correct interpretation and avoiding deceptive representations of information. By skillfully using these visualization instruments, we are able to remodel uncooked knowledge into compelling narratives that inform, persuade, and encourage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Unveiling Information: A Complete Information to Bar Graphs, Histograms, Line Graphs, and Pie Charts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!