Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Information to Pie Charts in Arithmetic
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Information to Pie Charts in Arithmetic
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Information to Pie Charts in Arithmetic. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Information to Pie Charts in Arithmetic
Pie charts, also called circle charts, are ubiquitous in information visualization. Their easy, visually interesting nature makes them a strong device for speaking complicated data shortly and successfully. Whereas seemingly simple, understanding the underlying arithmetic and the nuances of their building and interpretation is essential for correct information illustration and evaluation. This text delves deep into the world of pie charts, exploring their mathematical foundations, building strategies, benefits, limitations, and functions throughout numerous fields.
1. The Mathematical Basis: Proportions and Angles
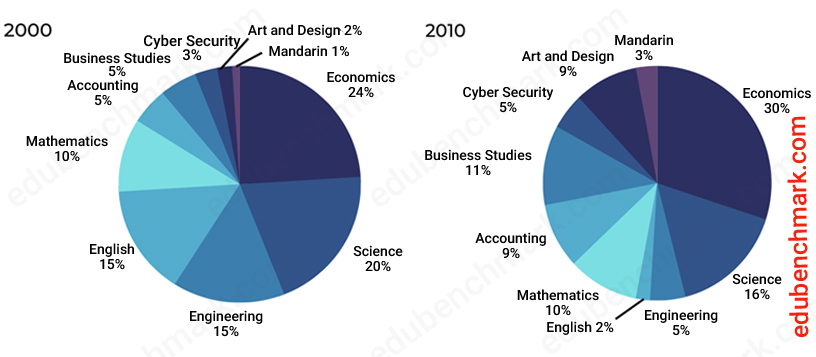
At its core, a pie chart is a graphical illustration of proportions. The complete circle represents an entire – 100% of the info being analyzed. Every phase of the pie, or "slice," corresponds to a selected class throughout the information set, its dimension instantly proportional to its relative contribution to the entire. This proportionality is translated visually by means of angles.
The mathematical precept governing the development of a pie chart is straightforward: the angle subtended by every phase on the heart of the circle is instantly proportional to the proportion of the info it represents. Since a circle encompasses 360 levels, every class’s angle is calculated as follows:
*Angle = (Class Worth / Complete Worth) 360°**
As an example, if a knowledge set reveals that 40% of respondents choose a selected model of espresso, the corresponding phase within the pie chart would have an angle of (0.40 * 360°) = 144°. This simple calculation ensures that the visible illustration precisely displays the quantitative relationships throughout the information.
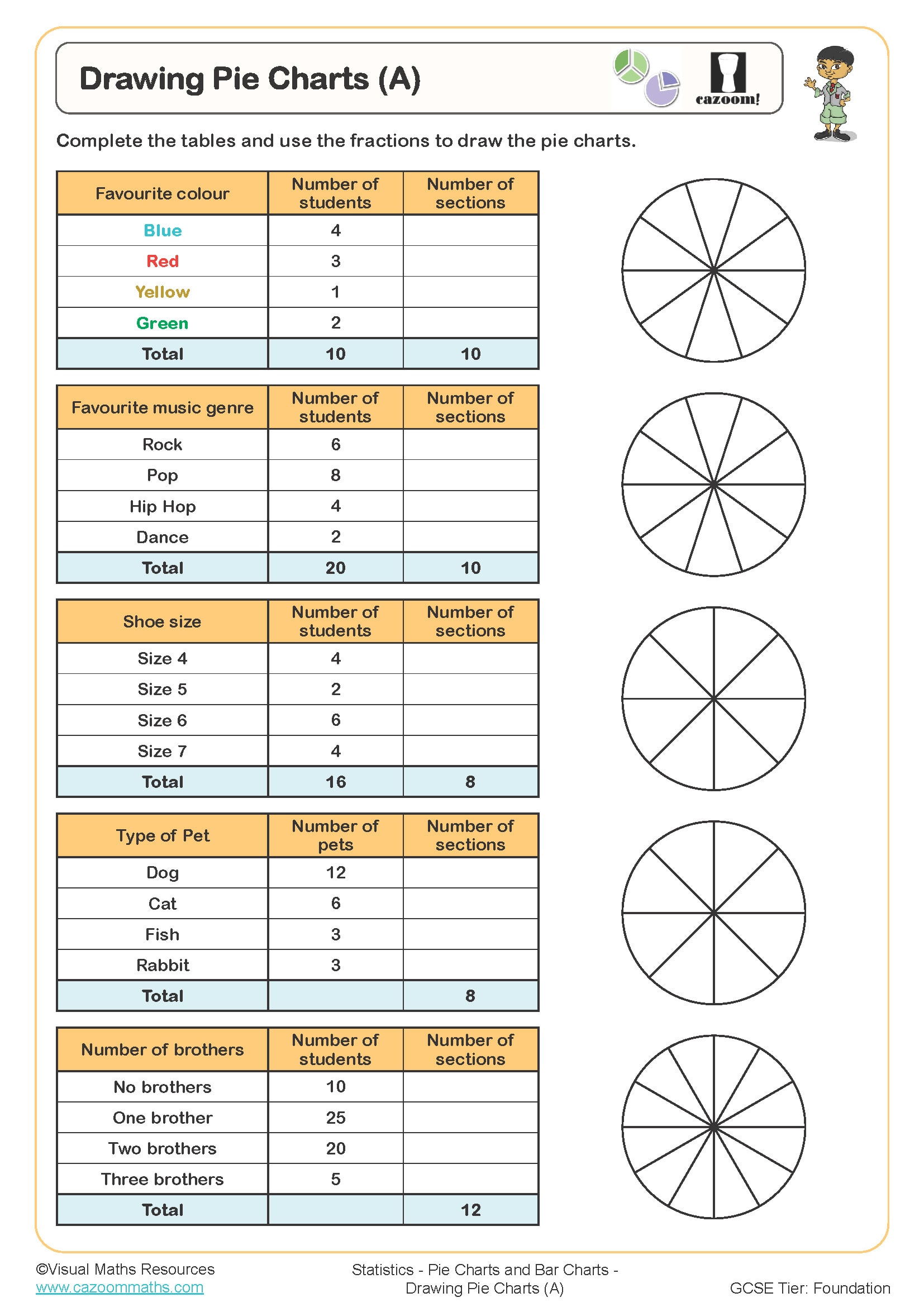
2. Developing a Pie Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Making a pie chart entails a number of steps, every requiring cautious consideration to element to make sure accuracy and readability:
-
Information Assortment and Group: Step one is to collect and manage the info. This entails figuring out the classes and their corresponding values. The info ought to be neatly tabulated for simple calculation and visualization.
-
Calculating Proportions: Decide the proportion every class contributes to the whole. That is carried out by dividing the worth of every class by the whole worth and multiplying by 100% to specific it as a proportion.
-
Calculating Angles: Utilizing the system talked about earlier, calculate the angle for every phase. This step is essential for correct illustration. A slight error in calculation can result in a deceptive visible illustration.
-
Drawing the Circle: Draw a circle utilizing a compass or an acceptable drawing device. The dimensions of the circle is unfair, nevertheless it ought to be massive sufficient to permit for clear labeling and differentiation of segments.
-
Dividing the Circle: Utilizing a protractor, rigorously measure and mark the calculated angles for every phase. Begin from a delegated level on the circle (e.g., the highest) and mark the angles consecutively.
-
Section Labeling: Label every phase clearly, indicating each the class title and its corresponding proportion or worth. This ensures that the viewer can simply perceive the data offered.
-
**Including a



![Bài mẫu IELTS Writing Task 1 #29 [Pie] Nguyễn Cảnh Tuấn](https://nguyencanhtuan.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Pie-24.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Information to Pie Charts in Arithmetic. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!