x vs y axis chart
Associated Articles: x vs y axis chart
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to x vs y axis chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Cartesian Aircraft: A Deep Dive into X vs. Y Axis Charts
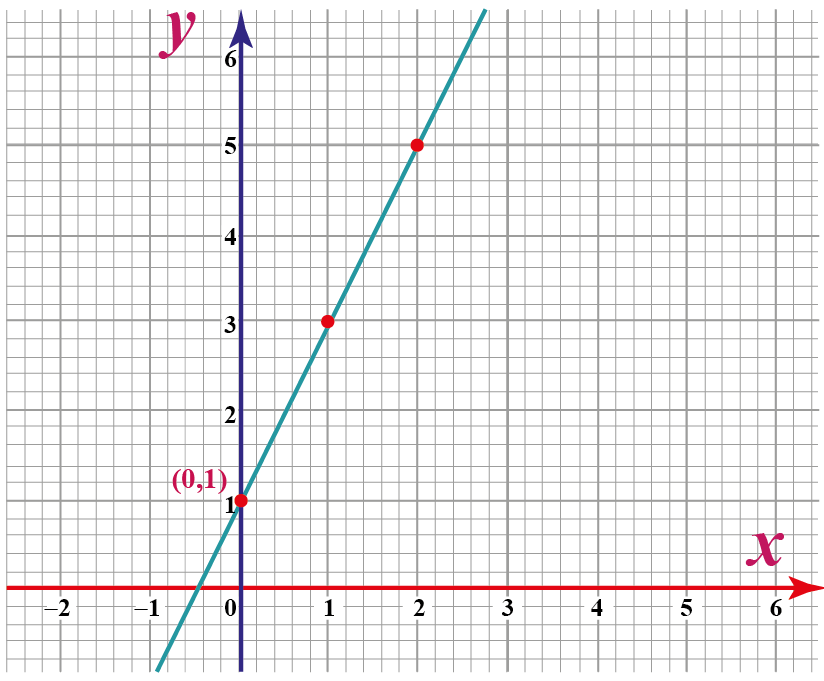
The common-or-garden x vs. y axis chart, also called a Cartesian coordinate chart or just a line graph (when depicting traces), is a cornerstone of information visualization. Its seemingly easy construction – two perpendicular axes intersecting at some extent of origin – belies its energy to characterize an enormous array of relationships between two variables. Understanding its nuances is essential for anybody working with information, from college students analyzing experimental outcomes to information scientists constructing predictive fashions. This text will delve into the intricacies of x vs. y axis charts, exploring their development, functions, interpretations, and limitations.
The Basis: Understanding Axes and Coordinates
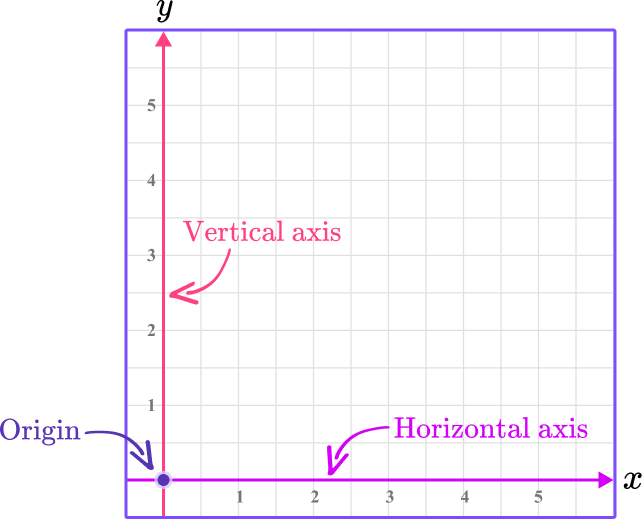
The Cartesian coordinate system, named after the famend mathematician René Descartes, makes use of two perpendicular traces, the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical), to outline a two-dimensional aircraft. The purpose the place the axes intersect is known as the origin, often denoted as (0,0). Every level on the aircraft is uniquely recognized by its coordinates – an ordered pair (x, y) representing its horizontal and vertical distances from the origin, respectively. The x-coordinate represents the place alongside the horizontal axis, and the y-coordinate represents the place alongside the vertical axis.
The selection of which variable to plot on which axis is essential. Usually, the unbiased variable – the variable that’s manipulated or managed – is plotted on the x-axis (the horizontal axis). The dependent variable – the variable that’s measured or noticed and whose worth is determined by the unbiased variable – is plotted on the y-axis (the vertical axis). For instance, in an experiment learning the impact of fertilizer on plant development, the quantity of fertilizer (unbiased variable) could be plotted on the x-axis, and the plant top (dependent variable) could be plotted on the y-axis.
Kinds of X vs. Y Axis Charts
Whereas the basic construction stays constant, x vs. y axis charts can take a number of types, every suited to various kinds of information and analytical objectives:
-
Line Graphs: These are used to show steady information, displaying the pattern or relationship between two variables over time or one other steady variable. They’re significantly helpful for highlighting traits, figuring out patterns, and making predictions. Line graphs are perfect for displaying modifications in a variable over time, equivalent to inventory costs, temperature fluctuations, or inhabitants development.
-
Scatter Plots: These charts show particular person information factors as dots on the aircraft. They’re helpful for exploring the correlation between two variables with out implying a causal relationship. Scatter plots reveal the energy and path of the connection (constructive, unfavorable, or no correlation). Outliers, information factors considerably deviating from the final pattern, are simply recognized in scatter plots.
-
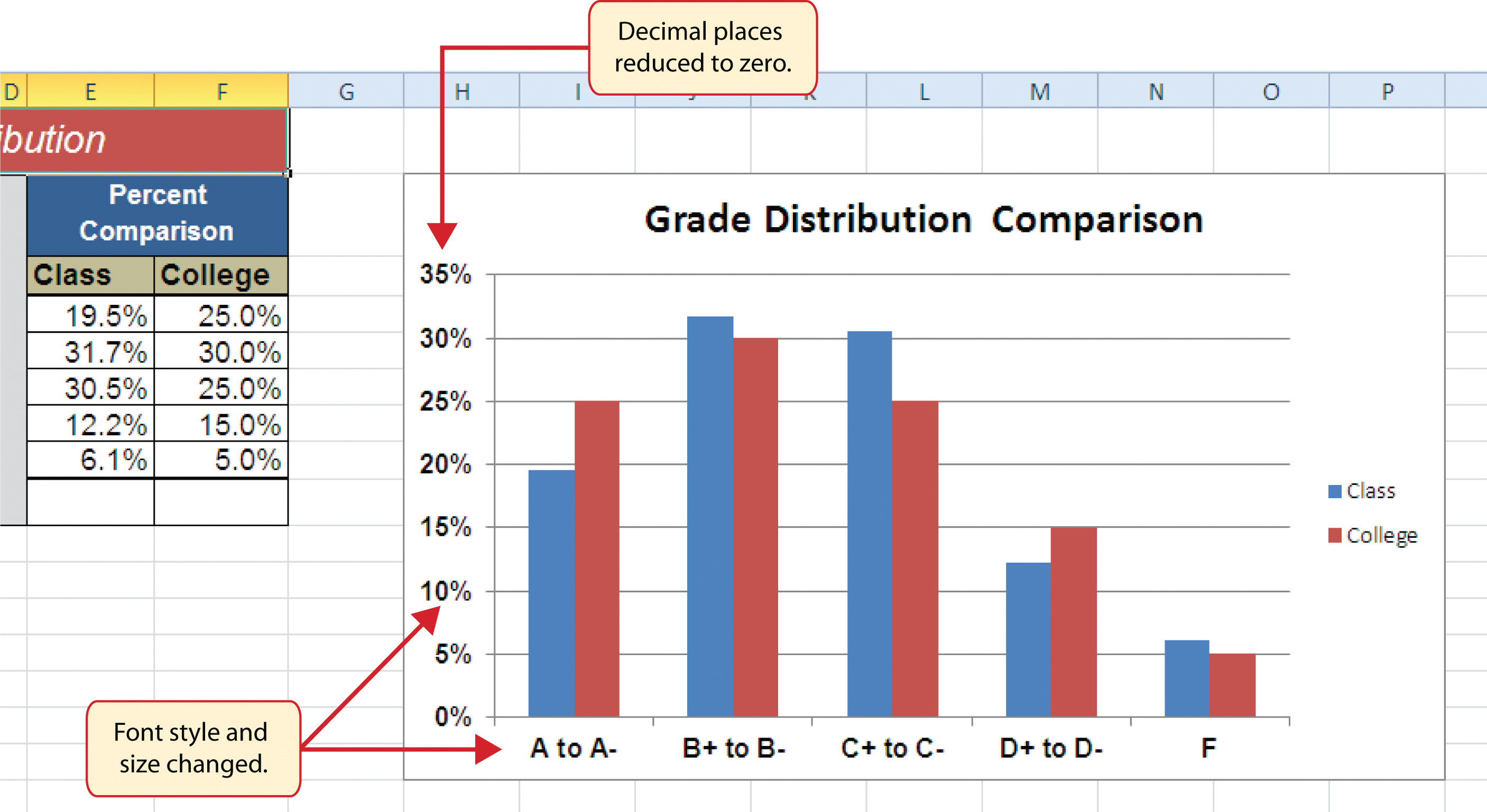
Bar Charts: Whereas technically not strictly x vs. y axis charts within the purest sense (as they do not characterize steady information), bar charts typically use the x-axis to characterize categorical variables and the y-axis to characterize the corresponding values. They’re efficient for evaluating values throughout completely different classes. For example, a bar chart might examine gross sales figures throughout completely different product traces.
-
Histograms: Just like bar charts, histograms characterize the frequency distribution of a single steady variable. The x-axis represents the vary of values, and the y-axis represents the frequency or depend of information factors inside every vary. Histograms are helpful for visualizing the distribution of information, figuring out skewness, and figuring out potential outliers.
Deciphering X vs. Y Axis Charts:
Deciphering x vs. y axis charts includes analyzing the patterns and relationships depicted. Key points to contemplate embody:
-
Pattern: Does the info present an upward pattern, a downward pattern, or no discernible pattern? A constructive pattern signifies a constructive correlation (as x will increase, y will increase), whereas a unfavorable pattern signifies a unfavorable correlation (as x will increase, y decreases).
-
Correlation: How sturdy is the connection between the 2 variables? A robust correlation means the factors cluster carefully round a line or curve, whereas a weak correlation means the factors are extra scattered.
-
Outliers: Are there any information factors that considerably deviate from the general pattern? Outliers can point out errors in information assortment, uncommon occasions, or probably essential insights.
-
Slope: In line graphs, the slope of the road represents the speed of change of the dependent variable with respect to the unbiased variable. A steeper slope signifies a quicker charge of change.
-
Intercepts: The y-intercept (the purpose the place the road crosses the y-axis) represents the worth of the dependent variable when the unbiased variable is zero.
Limitations of X vs. Y Axis Charts:
Whereas highly effective, x vs. y axis charts have limitations:
-
Overplotting: In scatter plots with many information factors, overplotting can obscure the underlying patterns. Strategies like jittering or transparency can mitigate this subject.
-
Deceptive scales: Manipulating the dimensions of the axes can distort the notion of the connection between variables. It is essential to make use of acceptable scales and clearly label the axes.
-
Causation vs. correlation: Correlation doesn’t suggest causation. Even a robust correlation between two variables does not essentially imply that one variable causes the opposite. Different elements could also be influencing each variables.
-
Restricted dimensionality: X vs. y axis charts can solely characterize relationships between two variables. For analyzing relationships involving greater than two variables, extra refined methods like 3D plots or multivariate evaluation are crucial.
Superior Purposes and Extensions:
The fundamental x vs. y axis chart types the inspiration for a lot of extra advanced visualization methods. These embody:
-
Regression evaluation: Becoming a line or curve to the info factors in a scatter plot to mannequin the connection between the variables.
-
Time collection evaluation: Analyzing information collected over time to establish traits, seasonality, and different patterns.
-
Management charts: Monitoring processes over time to detect variations and establish potential issues.
-
Geographic Info Techniques (GIS): Utilizing x and y coordinates to characterize places on a map.
Conclusion:
The x vs. y axis chart is a basic device for information visualization, providing a easy but highly effective strategy to characterize the connection between two variables. Understanding its development, interpretation, and limitations is essential for efficient information evaluation. By rigorously choosing the suitable chart kind, selecting acceptable scales, and critically deciphering the outcomes, we will leverage the ability of x vs. y axis charts to achieve beneficial insights from information. Nevertheless, it’s important to keep in mind that these charts are just one piece of the puzzle, and needs to be used at the side of different analytical strategies for a complete understanding of the info. Moreover, at all times take into account the context of the info and the potential limitations earlier than drawing conclusions primarily based on the visualization alone.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into x vs y axis chart. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!